There is often some confusion about the difference between Scandinavian and Nordic countries. Are ‘Scandinavian’ and ‘Nordic’ the same thing? And if not, which countries are Nordic but not Scandinavian?

Of course, people living in the Nordic region know the difference, and can easily tell you whether or not their country is part of Scandinavia! But for first-time visitors, it can all get a bit confusing.
How many Scandinavian countries are there?
Some people believe that there are five Scandinavian countries, but the general consensus within Scandinavia itself is that there are three: Norway, Denmark and Sweden.
If we look at it geographically, however, the Scandinavian peninsula is actually only home to two countries – Sweden and Norway – though it also includes the northern tip of Finland.
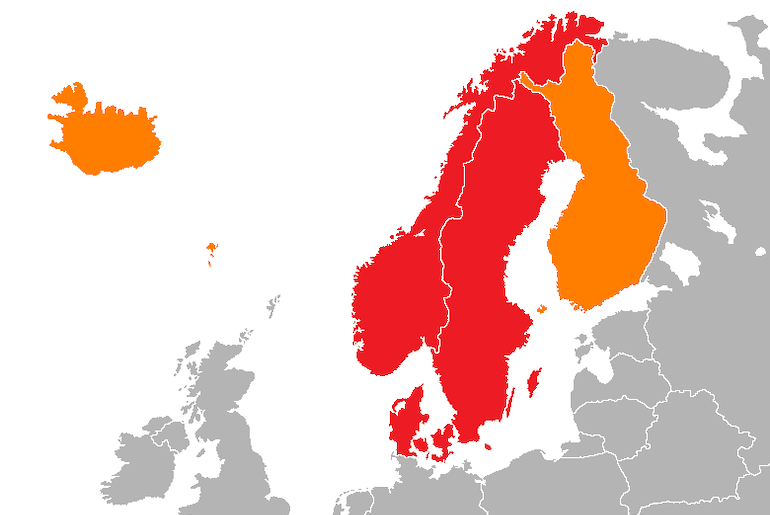
TIP: For more on the Scandinavian peninsula, its history and significance, read this guide.
Although Denmark is not actually on the Scandinavian peninsula, it is definitely considered part of Scandinavia as it is culturally and historically close to its neighbours Norway and Sweden: their languages share common characteristics and Denamrk used to control large sections of Sweden.
Alright, so how many Nordic countries are there?
So, the general consensus is that there are five Nordic countries – Norway, Sweden, Denmark, Finland and Iceland.
This is the three Scandinavian countries PLUS Finland and Iceland, which share many aspects of Norse history and culture.
These five countries make up the Nordic Council, the official body that exists to promote inter-parliamentary co-operation, integration and trade between the Nordic countries.
For more on the difference between the Nordic and Scandinavian countries read our quick guide to the Scandinavian countries.
So what is the difference between Nordic vs Norse?
Nordic is the adjective used to describe anything related to the Nordic countries, ie: Norway, Sweden, Finland, Denmark and Iceland.
So we can talk about Nordic design, Nordic culture and Nordic cuisine to describe aspects that all five countries have in common.
Norse is a different word used to refer to the ancient people who were native to these five countries and their common culture.

Norse is often used interchangeably with Viking to describe the Germanic people who lived in Scandinavia in Viking times and went on to spread their culture and language to the other Nordic countries. Many people across the Nordic countries have Norse names, for example.
Do all Nordic countries have Viking heritage?
The Vikings originated in what is now Denmark, Norway and the south of Sweden. They were great traders and seafarers who travelled west to trade with and colonise other lands, including Iceland.
Most Icelandic men are descended from Norwegian Vikings, though most Icelandic women came from the British Isles – some voluntarily, and others who had been kidnapped or traded by the Vikings.
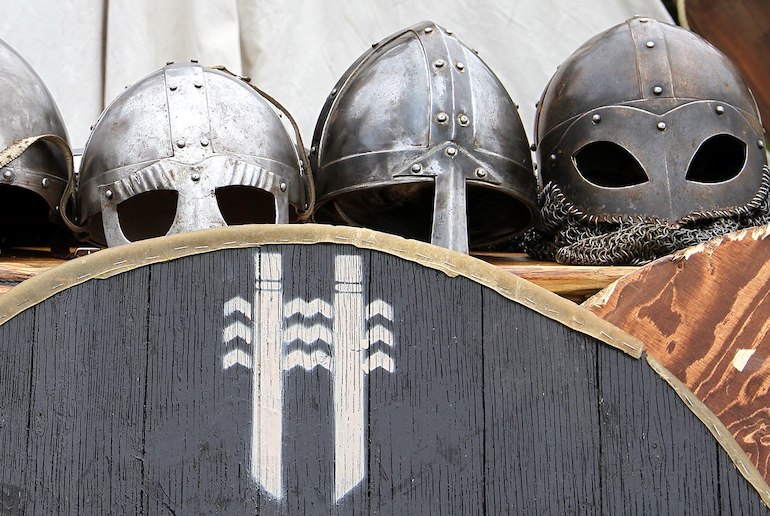

Like the north of Sweden, Finland was mostly populated by indigenous Sami and there is little evidence of Viking settlements.
The Vikings traded at ports along Finland’s southern coast en route to Russia, but didn’t seem to venture further inland.
Whether the Vikings found little of interest to trade in the Finnish interior or whether the terrain and climate was too harsh is unknown.
What is the difference between Nordic and Scandinavian design?
There is a lot of overlap when you’re considering Scandinavian vs Nordic design.
Both feature clean strong lines and a minimalist aesthetic, with an emphasis on natural light and the use of natural materials and colours.
However, there are also subtle differences between the two styles. Some designers feel that Scandinavian design is more minimalist with functionality at its core, while Nordic design is more homely and influenced by traditional workmanship and crafts.
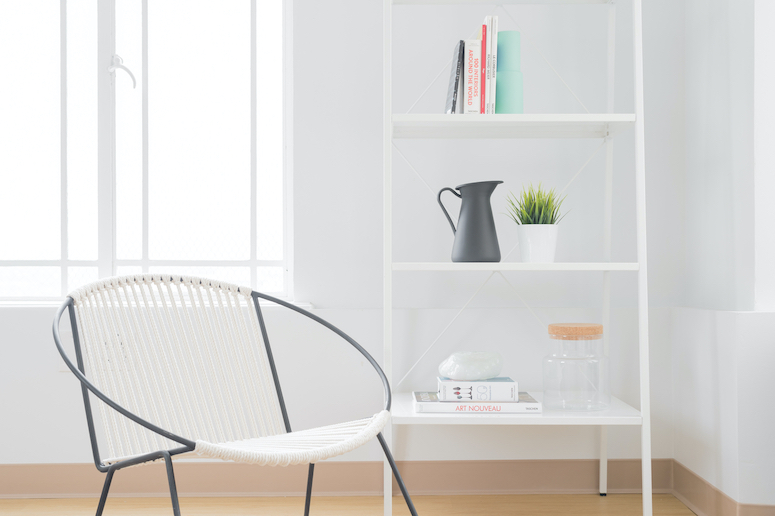

In Nordic design, the neutral tones are often contrasted with a splash of colour and comfort, such as a traditional brightly coloured blanket.
On the other hand, some designers feel that Scandinavian designs are more tactile and comfortable, while others use the two terms interchangeably!
So, in reality both terms refer to a similar aesthetic that took root in the Nordic countries in the early twentieth century and continues to gain increasing popularity around the world.
Is Estonia Nordic?
So, what about the Baltic countries? Are Estonia, Lithuania and Latvia considered Nordic countries?
The Baltic states have traditionally had close cultural and trade links to Scandinavia, while Estonia and the northern part of Latvia were ruled by Sweden for many years.
As the northernmost Baltic state, Estonia has long had strong ties with Finland in particular, and its people and language are Finnic in origin.
Since the break-up of the USSR, there has been a growing movement in Estonia to re-establish its Nordic allegiances and to join the Nordic Council. However, Estonia is currently not considered a Nordic country, but rather a Baltic state like Latvia and Lithuania.
Is Greenland Nordic?
As an independent protectorate of Denmark, Greenland is considered a Nordic country, but not part of Scandinavia.
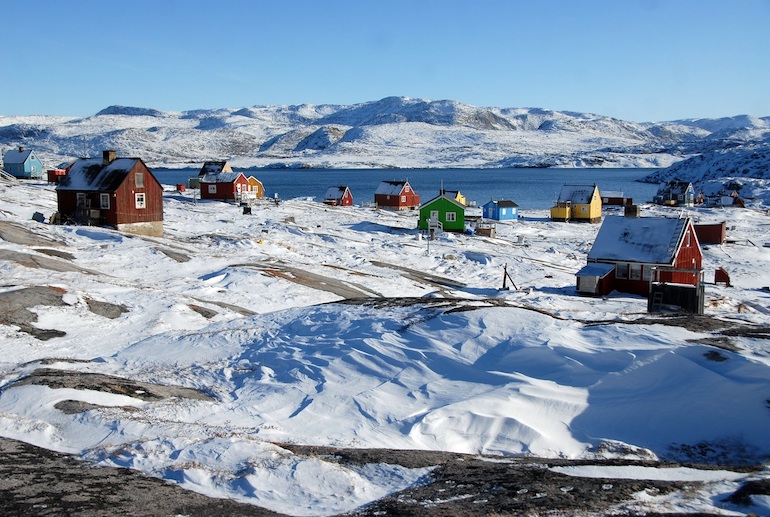

In its official classification of Nordic countries, the Nordic Council includes Denmark, Norway, Sweden, Finland and Iceland, plus the Faroe Islands, Greenland and the self-governing Åland islands (which lie in the Gulf of Bothnia between Finland and Sweden).
Do all Scandinavian countries accept Euros?
None of the Scandinavian countries have adopted the Euro as their official currency.
Of the Nordic countries, Finland is the only country to officially use the Euro, while all the others have retained the ‘crown’ as their currency.
Sweden uses the Swedish krona, Denmark uses the Danish krone, Norway uses the Norwegian krone, and Iceland uses the Icelandic króna.
Which Scandinavian countries are in the EU?
Of the Scandinavian countries, Denmark and Sweden are both members of the EU, while Norway is not.
If we’re looking at all the Nordic countries, Iceland and Norway are not in the EU, but Finland, Sweden and Denmark are.
Although not in the EU, both Iceland and Norway are part of the EEA (European Economic Area) and signatories to the Schengen Agreement, which allows free movement of people within Europe.
See also:
The best places to visit in Scandinavia
Scandinavian Flags: all you need to know
Quick Guide to the Scandinavian countries
What is the Scandinavian peninsula?









